Mathematics GCSE and IGCSE Formulae Sheet
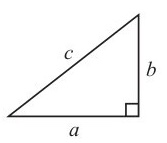
Pythagoras' Theorem
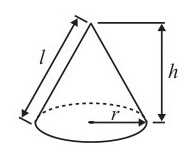
Volume of a cone =
Curved surface area of a cone =
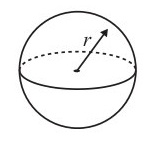
Volume of a sphere =
Surface area of a sphere =
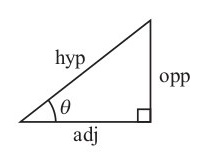
Or
In any triangle
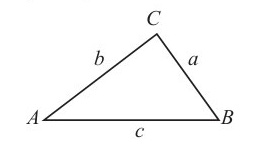
Sine rule:
Cosine rule:
Area of a triangle =
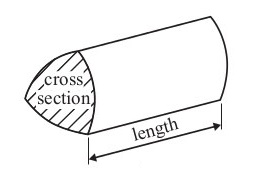
Volume of a prism = area of cross section
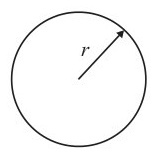
Circumference of a circle =
Area of a circle =
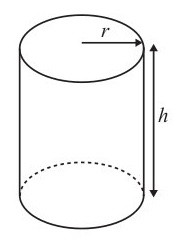
Curved surface area of a cylinder =
Volume of a cylinder =
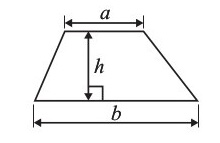
Area of a trapezium =
The Quadratic Equation
The solutions of
where
Arithmetic series
The sum of
Compound interest
Where
Total accrued
Probability
Where


